Recent press coverage has focused a lot of attention on some long-hidden vulnerabilities in firewalls. Network security teams are scrambling to understand whether they are exposed, and to what extent. These notes show how you can use RedSeal to understand the extent of the problem in your specific network.
Nature of the Issues
The current focus is on a set of newly publicized vulnerabilities that had not been uncovered previously, including this Cisco advisory for their ASA products: https://tools.cisco.com/security/center/content/CiscoSecurityAdvisory/cisco-sa-20160817-asa-snmp
This is not the only vulnerability found in the “Shadow Broker” files, but serves as a good working example. The nature of the vulnerability is a flaw in SNMP, which is very commonly used as an important function of network infrastructure. Simply disabling SNMP is not generally a viable workaround, since SNMP is a vital part of network visibility. (Even if your windshield has a crack in it, it’s not a good response to paint it black.) Instead, organizations have to understand whether they have properly limited access to the vulnerable protocol, and where the locations are that need access.
In other words, a network is in poor shape if anyone, anywhere inside the network can use SNMP to communicate with the firewalls. In that scenario, an attacker anywhere inside the organization can compromise a firewall — an extremely undesirable situation. Such an attacker can surreptitiously monitor traffic, since firewalls are often at critical choke points in networks with a view into all boundary-crossing flows. Worse, if the attacker wants to be disruptive to operations, there are few locations as powerful as a main firewall to cut off the ability of an organization to function and respond.
A well-built organization does not allow SNMP access from anywhere to their key network infrastructure. Instead, they limit access, since SNMP is useful, but not needed by most people in an organization to do their jobs. It has long been a best practice in network architecture to limit access for SNMP only to those locations that need it. But which locations are those exactly? An organization responding to the “Shadow Broker” disclosures has to scramble to quickly understand where they allow SNMP, since these locations are the critical attack surface for these newly revealed attacks.
Finding Access to Firewalls
With RedSeal, it’s very easy to find out whether you are wide open to these SNMP attacks, and if not, to locate where you allow access.
Step 1: Bring up the Security Intelligence Center, using the yellow light bulb icon in the icon bar:
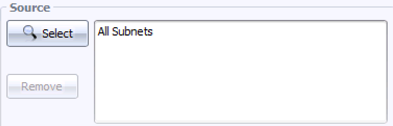
Step 2: On the left, under Source, click Select, then Browse, then All Subnets, then Replace. This sets the source for the query to “anywhere”. You should see this:
Step 3: On the right, under Destination, click Select, then Browse, and change the View to Primary Capability. Open the Firewall folder, like this:
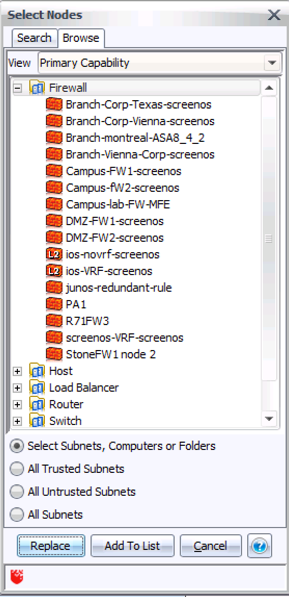
Step 4: To start with, pick just one firewall – in this example, I’ll take the second one on the list, from Vienna. Hit Replace to add this to the query dialog.
Step 5: In the Protocols field, enter “udp” (without the quote marks) and in the Ports field, enter “161”. This is the port and protocol for basic SNMP communication. The query dialog now looks like this:
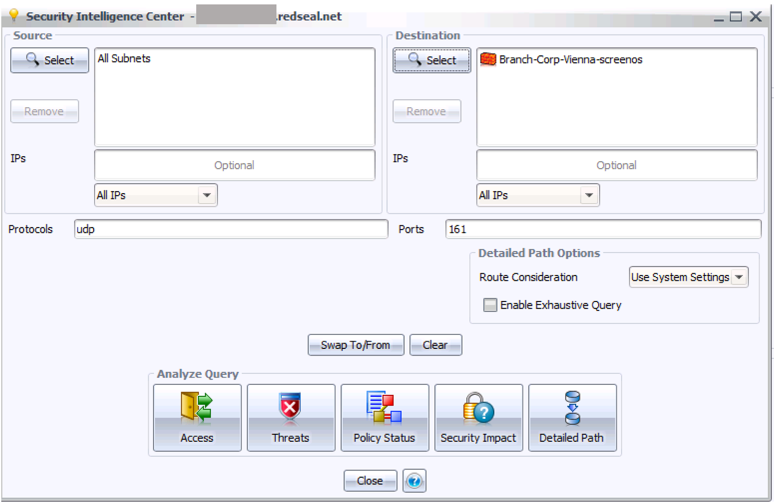
Step 6: Click the Access button in the icon bar at the bottom. This will show you a table of all access to the given firewall – in this case, just one row:
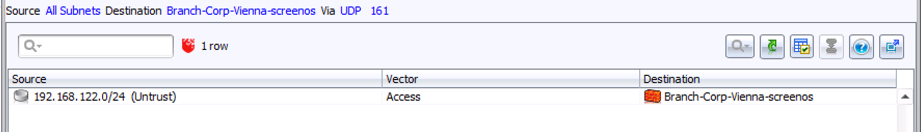
Step 7: To see this visually, click “Show In Topo” at the bottom of this result. This will take you to the network map, and highlight where you have SNMP access to the firewall.
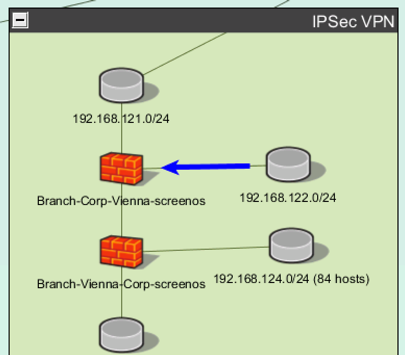
This is a “good” result. Only one location in the network can use SNMP to reach this firewall. There is still risk – it’s important to investigate any defects, vulnerabilities, or indicators of compromise from the source side of this arrow. But fundamentally, this firewall was secured following best practices – the total amount of the network that can access the SNMP management plane of this device is very limited.
However, in real world networks, the answer will often be messier. RedSeal recommends following the above steps for only one firewall at first, to look at the extent of SNMP access. If your organization shows a good result for the first few firewalls, this is reassuring, but can then lead to harder questions. For example, we can ask a much wider question, covering all the firewalls at once. This should only be attempted after looking at a few individual firewalls, since the full query can generate an overwhelming amount of data.
To ask this broader question, go back to step 4 – in the Security Intelligence Center dialog, click Select on the right, under Destination. Rather than picking one firewall off the list, we can select the folder of all firewalls, then click Replace. The query dialog now looks like this:
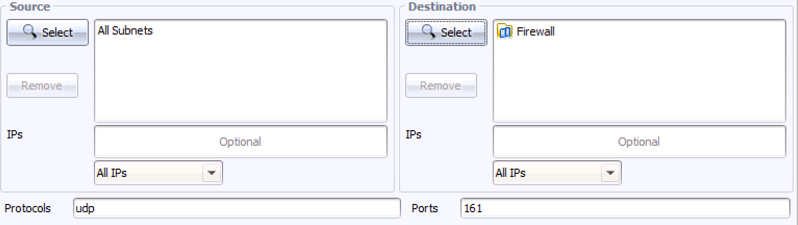
Even in a relatively small network, this generates a lot of information. We can look at the answer visually, using Show in Topo:
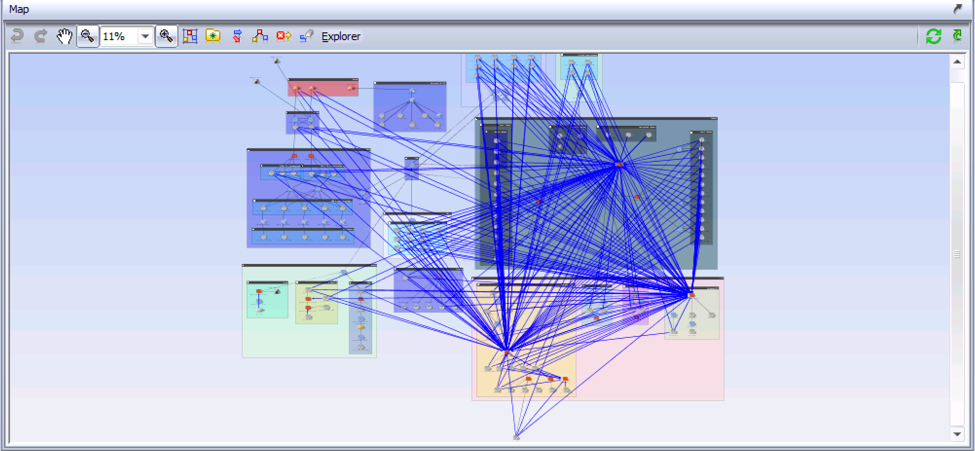
Clearly, this network has not followed the best practice design of limiting access to all firewalls. Each blue arrow represents some location that has access to a firewall over SNMP. It is not plausible that so many locations in this network need that access to perform their job functions. This network needs to focus on internal segmentation.
Checking Firewall Code Versions
As the various vendors release updates, it’s important to track whether you have firewalls that need to be updated urgently – especially those with very wide access. You can use RedSeal to generate a summary report on the types of firewalls you have, and which versions of software they are running. One way to report on firewalls by version is as follows:
Step 1: Open Reports tab, select Security Model in the left hand list of reporting areas.
Step 2: Click the + button to create a new report, and select a data type of Network Device
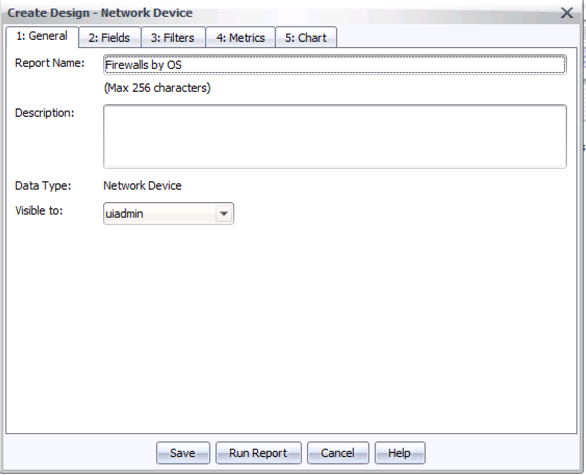
Step 3: On the first tab, name your report “Firewalls by OS” (without the quotes – or pick your own name for the report), like this:
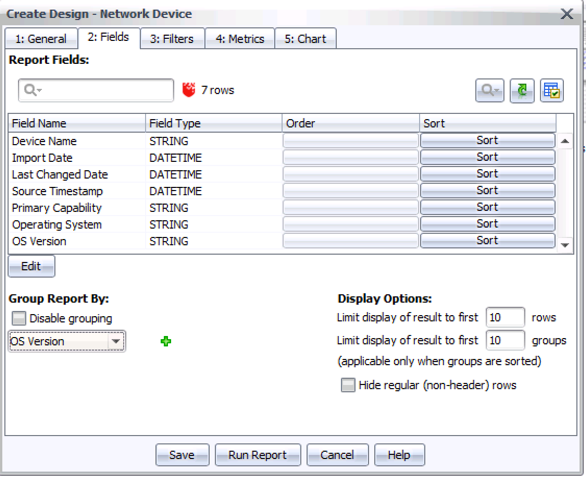
Step 4: On the second tab (Fields), click Edit, select OS Version on the left list, and click Add to add it to the list of fields in the report. Click OK.
Step 5: Under Group Report By, change the grouping to “OS Version”
Step 6: Under Display Options, enter 10 in “Limit display of results to the first N rows”. (This is to abbreviate the report, at least initially. Some organizations have a great many firewalls, and the first thing to do is to figure out which OS versions you have, with a few listed examples, before digging through too large of an inventory report.)
By this point, tab 2 should look as follows:
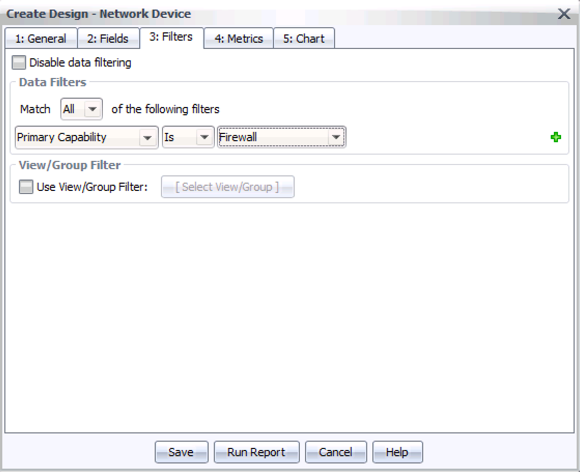
Step 7: Change to tab 3, Filters, and under “Match All”, add a rule for “Primary Capability”, then “Is”, then “Firewall”, like this:
Step 8: Hit Save. The default choices on tabs 4 and 5 will work well here, to include some counts and a chart.
Step 9: On the Reports tab, run your new report by double-clicking the icon above “Firewalls by OS” (or whatever name you gave your report).
Your browser will pop up requesting log in (if you haven’t logged in previously), then will display a report summary chart like this:
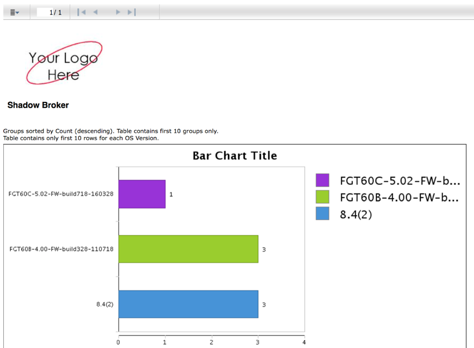
You may want to focus first on the smaller bars – the unusual outliers in your network infrastructure. This is where overlooked problems – in this case, well down-rev firewall operating systems – can lurk. The report details will include a sample of the firewalls running each code image in your environment, like this:
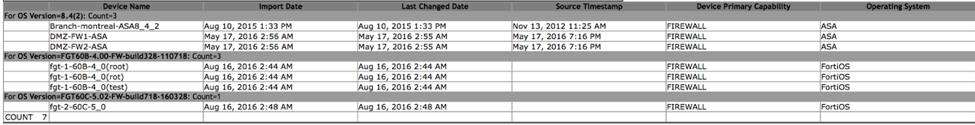
As the firewall vendors move to produce new releases to close off these vulnerabilities, you can use a report like this to track how well your operational teams are deploying these important updates.
Conclusions
The recently uncovered vulnerabilities, which appear to have been in use for many years, are further proof that we need to keep our houses in order. An organization with good discipline about internal segmentation, with a well separated network management infrastructure, has less to worry about with these new revelations. But even that organization needs rapid ways to assess whether the discipline has really held up in practice. Are there gaps? If so, where? Even the locations that do have SNMP access to firewalls, are they easy or hard for an attacker to break into? All of these questions are easy to answer if you have the ability to analyze your as-built, rapidly evolving network infrastructure. RedSeal makes it easy to find answers to these vital questions.


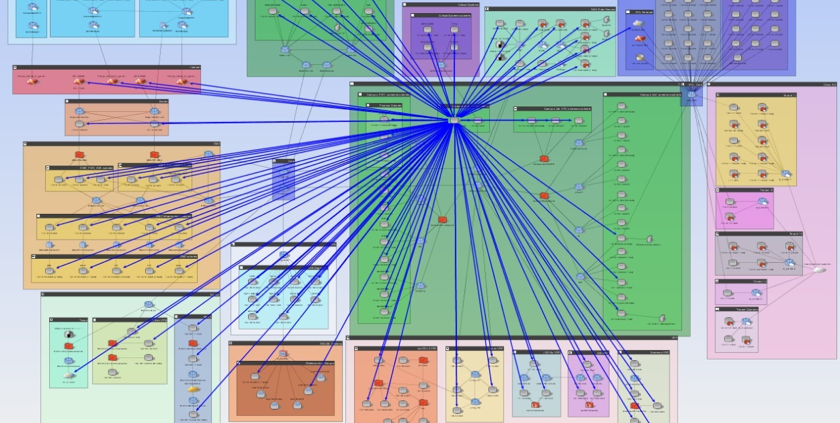
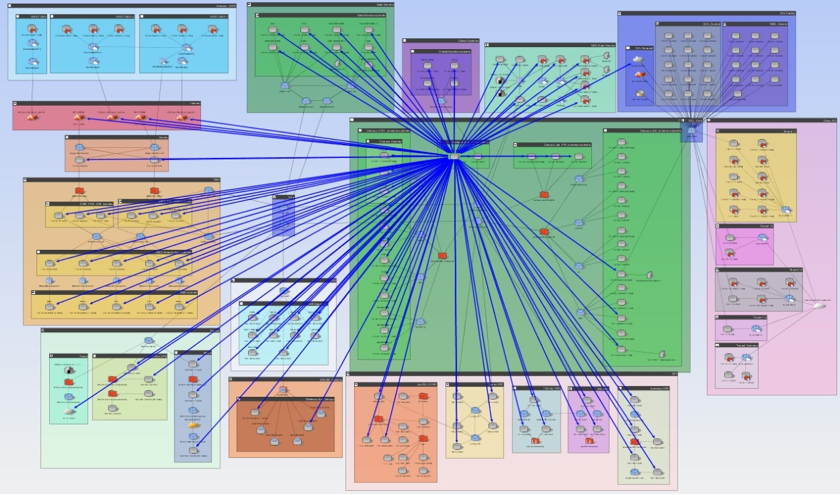 Figure 1: Visualizing all accessible areas of the network from a compromised system.
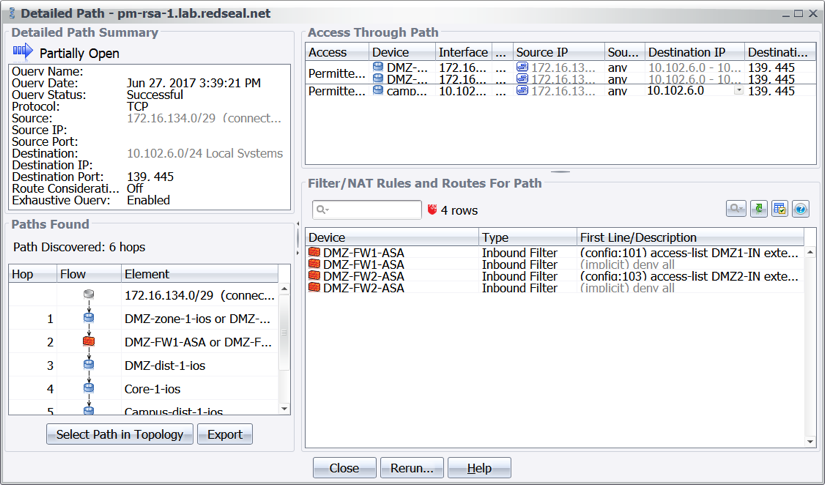
Figure 1: Visualizing all accessible areas of the network from a compromised system.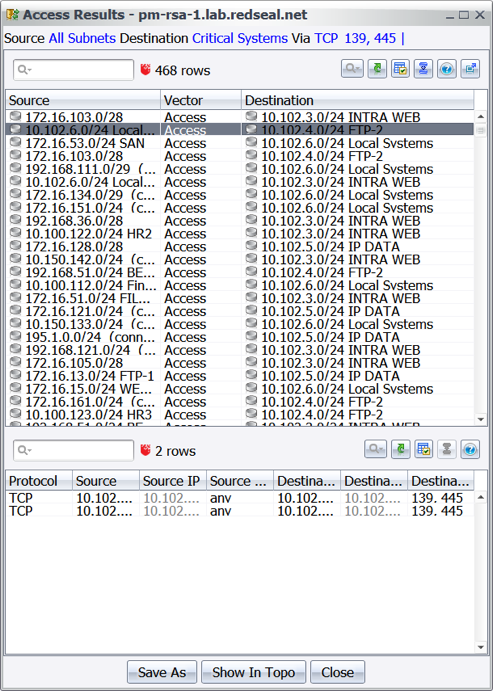 Figure 2 Results of an access query revealing what access exists from all subnets leading to the critical assets over TCP 139 or 445.
Figure 2 Results of an access query revealing what access exists from all subnets leading to the critical assets over TCP 139 or 445.