Cyber News Roundup for May 9, 2024
Cuckoo malware, a paralyzed city of Wichita, and early cybersecurity preparations for the upcoming Olympics made headlines this week. RedSeal is here to keep you informed and equipped to fortify your cyber defenses in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
1. Cuckoo malware targets macOS systems
Cybersecurity researchers at Kandji have identified a new malware called Cuckoo targeting Apple macOS systems. It’s designed as a universal Mach-O binary, compatible with both Intel and ARM-based Macs, and found on websites offering music ripping and MP3 conversion tools. Cuckoo establishes persistence via a LaunchAgent and employs a locale check to avoid execution in Russia or Ukraine. It tricks users into providing system passwords through fake password prompts for escalated privileges and performs extensive data harvesting. This includes capturing hardware information, running processes, installed apps, screenshots, and sensitive data from iCloud Keychain, Apple Notes, web browsers, crypto wallets, and various applications like Discord and Steam. The associated malicious application bundles are signed with a valid developer ID. (Kandji)
2. Secretary of State Blinken is set to unveil a new international cybersecurity strategy at the RSA Conference in San Francisco
The Biden administration is set to introduce a new international cybersecurity strategy, marking the first U.S. global cyber strategy in over a decade, aimed at bolstering global cooperation against cyber threats. Secretary of State Antony Blinken will unveil the strategy at the RSA Conference in San Francisco. This strategic plan targets enhancing cybersecurity through four main pillars: establishing a secure digital ecosystem, promoting rights-respecting digital technology with allies, forming coalitions against cyberattacks, and boosting cybersecurity resilience among partner nations. A key element of this strategy is the allocation of $50 million to the newly formed Cyberspace and Digital Connectivity fund, aimed at supporting cybersecurity improvements in allied countries.
Additionally, the strategy emphasizes a proactive role in cyber diplomacy at the United Nations and seeks to develop global norms for emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI). The U.S. aims to foster international consensus on AI usage and cyber conduct. The strategy’s implementation is considered urgent, with efforts intensifying in the months leading up to the November presidential election, reflecting the need for consistent U.S. leadership in global cybersecurity irrespective of potential administration changes. (Politico)
3. Chinese-linked ArcaneDoor targets global network infrastructure
A new cyber espionage campaign named ArcaneDoor, potentially linked to Chinese actors, has targeted network devices from vendors like Cisco, starting in July 2023 with the first attack detected in January 2024, according Censys. The attacks involved custom malware, Line Runner and Line Dancer, and exploited patched vulnerabilities in Cisco Adaptive Security Appliances. The findings indicate the involvement of a China-based threat actor, given that key infrastructure used SSL certificates linked to Chinese networks and hosted services related to anti-censorship tools. (The Hacker News)
4. Largest city in Kansas paralyzed by ransomware attack
Another city government faces the implications of a ransomware attack. The city of Wichita, Kansas was forced to shut down portions of its network over the weekend after its IT systems were encrypted with ransomware. Bleeping Computer reports: payment systems for city water, court citations, and tickets are down. There is no additional information regarding whether any information was compromised or which ransomware group has claimed responsibility for the attack. (Bleeping Computer)
5. Microsoft warns Android developers to steer clear of the Dirty Stream
Microsoft has issued a warning to Android app users and developers about a new attack method called Dirty Stream, which exploits a path traversal vulnerability within Android’s content provider component, particularly the ‘FileProvider’ class. This vulnerability can lead to the takeover of apps and theft of sensitive data. Notably affected are popular apps like Xiaomi File Manager and WPS Office, which together boast over 1.5 billion installs. The vulnerability has been identified in applications totaling four billion installations and could potentially be present in other apps. Dirty Stream allows malicious apps to overwrite files in another app’s directory, facilitating arbitrary code execution and token theft. This can give attackers complete control over the app and access to user accounts. Microsoft has informed affected developers, who have patched their apps, and urges all developers to review their apps for this security flaw. Google has also published guidance for developers on handling this issue. (Security Week)
6. French cybersecurity teams prepare for “unprecedented” Olympic threat
Jérémy Couture, who is in charge of the cybersecurity hub for the event being held in Paris in July, says his goal is to have his team’s activities perceived as a “non-event” by successfully fending off attacks from nation state actors, hacktivists, thrill seekers, and everyone else. He adds that it’s not just the games themselves that need protecting, but also the infrastructure that supports them, such as transport networks and supply chains. Russia, which is banned from these games, is of particular focus, but, officials state, they are looking at everything. (Security Week)
7. Ascension health system disrupted by cyberattack
US health system Ascension has sustained a cyberattack that disrupted some of its systems, the Record reports. The organization, which runs 140 hospitals across the country, stated, “Our care teams are trained for these kinds of disruptions and have initiated procedures to ensure patient care delivery continues to be safe and as minimally impacted as possible. There has been a disruption to clinical operations, and we continue to assess the impact and duration of the disruption.” The nonprofit is working with Mandiant to respond to the incident. (The Record)
8. Mobile medical provider DocGo discloses data breach
Mobile health service provider DocGo has disclosed a cyberattack that led to the theft of patient health information, BleepingComputer reports. The company stated in an SEC filing, “Promptly after detecting unauthorized activity, the Company took steps to contain and respond to the incident, including launching an investigation, with assistance from leading third-party cybersecurity experts, and notifying relevant law enforcement. As part of its investigation, the Company has determined that the threat actor accessed and acquired data, including certain protected health information, from a limited number of healthcare records within the Company’s U.S.-based ambulance transportation business, and that no other business lines have been involved.”(Bleepingcomputer)
9. MedStar Health sustains breach
Maryland-based healthcare organization MedStar Health sustained a data breach affecting more than 183,000 patients, the Record reports. A hacker gained access to the data through email accounts belonging to three MedStar employees. The threat actor was able to access “patients’ names, mailing addresses, dates of birth, date(s) of service, provider name(s), and/or health insurance information.”The company said in a breach notification, “Patients whose information may have been involved are encouraged to review statements they receive related to their healthcare. If they identify anything unusual related to the healthcare services or the charges for services, they should contact the healthcare entity or health insurer immediately.” (The Record, MedStar Health)
10. US indicts LockBit ransomware ringleader
On Tuesday, the U.S. Department of Justice (DoJ) charged the mastermind behind the notorious LockBit ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) operation. The DoJ unmasked 31-year-old Russian National, Dimitry Yuryevich Khoroshev (also known as LockBitSupp, LockBit, and putinkrab) in a 26-count indictment that includes charges of fraud, extortion, and damaging protected computers. The charges carry a combined maximum penalty of 185 years in prison. Khoroshev is accused of designing LockBit, recruiting affiliates and maintaining LockBit’s infrastructure and leak site. Khoroshev allegedly received over $100 million in proceeds from the ransom payments. The US is offering a reward of up to $10 million for information leading to Khoroshev’s arrest. Sanctions were also announced on Tuesday by the United Kingdom and Australia. (SecurityWeek)
11. CISA is moving the needle on vulnerability remediation
CISA launched its Ransomware Vulnerability Warning Pilot in January 2023, and issued 1,754 warning notices to entities with vulnerable internet-accessible devices in its first year. The agency said that nearly half (for a total of 852) of these notifications resulted in organizations either patching, briefly taking systems offline to fix the issue, or otherwise mitigating exploitable flaws. The pilot program is set to launch as a fully automated warning system by the end of next year.
Another CISA-led initiative called Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV), which the agency introduced in 2021, is also speeding up vuln remediation times. The KEV is designed to notify government agencies and enterprises of high-risk threats in the wild. Bitsight reported that critical KEVs are remediated 2.6 times faster than a non-KEV threats, while high-severity KEVs are fixed 1.8 times faster. Non-profits and NGOs are the slowest to remediate, while tech companies and insurance and financial firms are the fastest.(The Register and Dark Reading)
12. Lockbit takes credit for Wichita attack
The pernicious ransomware organization added the city of Wichita to its leak site, giving officials until May 15th to pay an unspecified ransom. We previously covered the city’s announcement of the attack over the weekend. In the wake of the attack, city officials say it can only accept cash or checks for all city services, although the city will not shut off water services as a result until regular payment methods come back online. This attack also comes on the heels of the US law enforcement agencies publicly naming the suspected leader of LockBit, Dmitry Khoroshev. (The Record)
Have questions? Reach out to RedSeal today to chat with one of our cybersecurity experts.


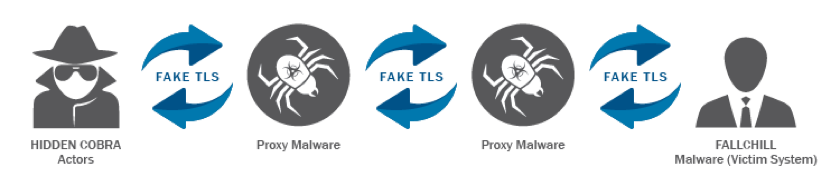
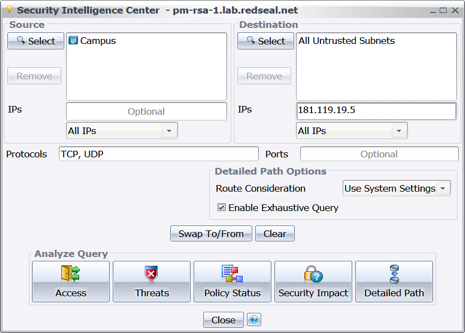
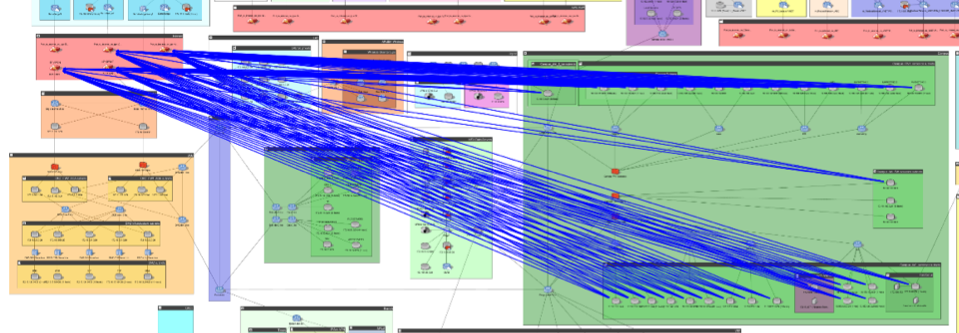
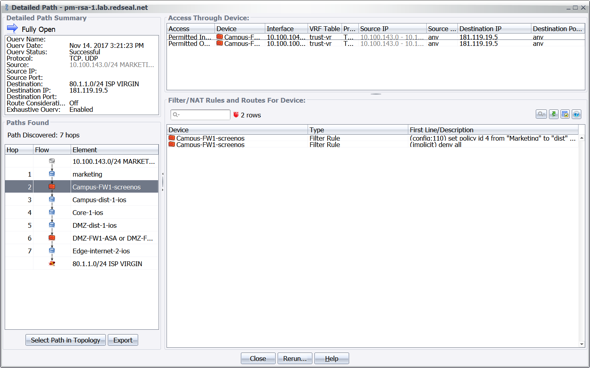
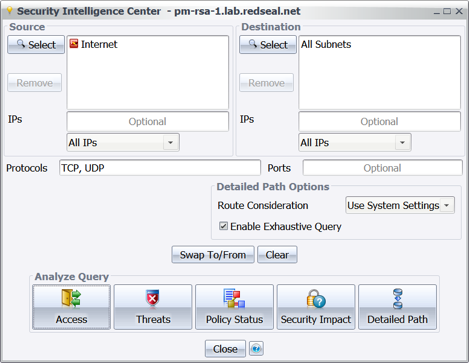
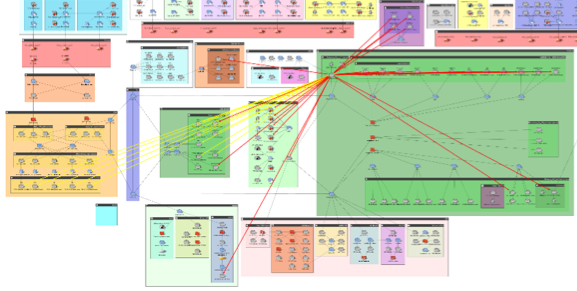
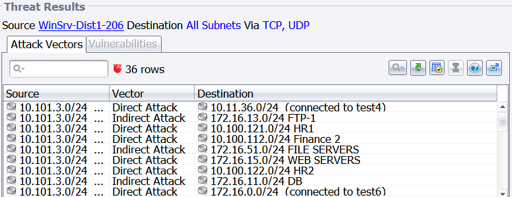
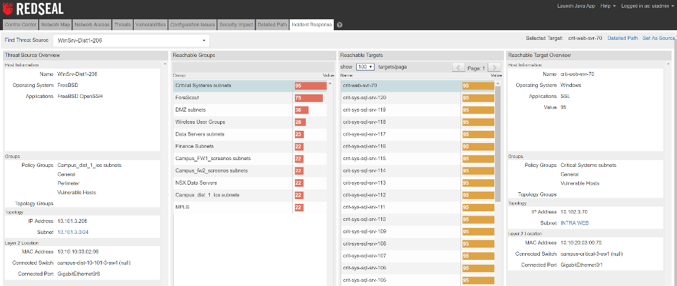
 Notably absent is the acknowledgement that the attack did not happen at a single point or computer, and that the actual theft of data was allowed because the data looked like legitimate network traffic using allowed routes through and out of the network.
Notably absent is the acknowledgement that the attack did not happen at a single point or computer, and that the actual theft of data was allowed because the data looked like legitimate network traffic using allowed routes through and out of the network. This attack unimagederscores two vital truths:
This attack unimagederscores two vital truths: